Moths in textiles
Moths (butterflies) are pests of both textiles and furs (including the Fur, Clothing and Wallpaper Moth) and food (including the Rye, Grain and Corn/Wheat Moth). However, this page focuses on the most common textile and fur pests in Finland, namely the fur and clothes moths. The tapeworm (Trichophaga tapetzella) has also been found in Finland, but its importance in our country is very limited.
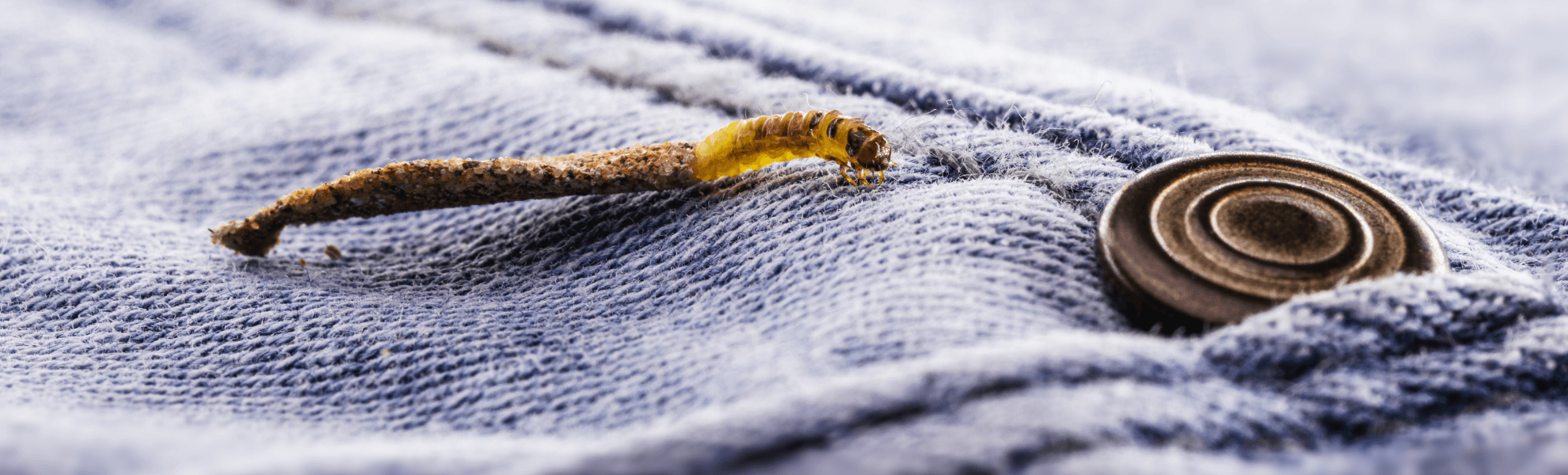
The clothes moth (Tineola bisselliella), unlike the fur moth, does not live in the wild in Finland. In warm indoor conditions, the clothes moth develops two generations per year. The larvae hatch from eggs laid by females on, for example, wool fabrics, furs and insulating materials, and weave a tube of fluff and webbing around them in which they live and move. It is from this webbing tube that the caterpillar can be easily identified.
In the past, the clothes moth was a common and nasty pest, but it has become less important in modern homes, where the central heating often used is apparently far too dry for it. Clothes moths usually enter the home either in the form of patches (e.g. a pillow or blanket stuffing) or in the form of accessories bought from abroad.
The fur moth(Tinea pellionella) larvae live in the wild in birds’ nests or in their waste, eating feathers, for example. From there, it may enter the house and damage natural fibres such as (wood) wool and fur.
Fur moth is even less important than clothing moth. It usually only wreaks havoc in the cold storerooms of museums and in the open air.

Tunnistus
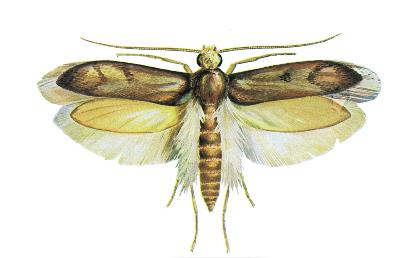
Both adult moths (fur and clothes moth) are relatively similar in size (wingspacing about 1.5 cm), so the best way to tell them apart is by their forewings.
The front wings of the fur coat are greyish yellow, while those of the clothes coat are straw yellow. Fur moths also have 1-2 dark spots on both wings, which are missing on the clothes.
The larvae of both are also relatively similar in size, 8-10 mm.

What can I do by myself?
Prevent damage to clothing by keeping your clothes clean, ventilating your home regularly and storing your non-regularly used textiles (clothes, blankets, sheets, blankets, etc.) in tightly sealed packages when you store them. All second-hand furniture and clothing should be washed (+60°C) and, if necessary, treated with a pesticide. In addition, all damp textiles should be dried and, if possible, the source of moisture removed.
If there are clothes moths flying in rooms, the first thing to do is to find out where they came from, i.e. the source of contamination. It can be a garment made entirely of natural fibres (e.g. wool), a fur coat or a recently used stuffed piece of furniture. Contaminated products must either be discarded, disinfected by washing (+60°C) or stored for a week in a freezer or in a constant hard frost (-25-30°C) outside. If necessary, we will help you!
If your moth problem cannot be solved by your own efforts and means, please contact us. We will solve it!

Pest control of clothing moths
First, the situation is analysed and an individual prevention plan is drawn up for the site. This is followed by an effective and high-quality pesticide treatment.
We use a variety of methods to achieve the best possible results as quickly as possible. We also try to avoid the use of biocides as much as possible.
For more information on the prevention methods we use, please contact our professional pest controllers. Contact us!

